Generic Medicines
Taj Pharma is the largest generic pharmaceutical company in India. We hold top positions in different established markets worldwide generics markets..
The Kingdom of Morocco is the most westerly of the North African countries known as the Maghreb.
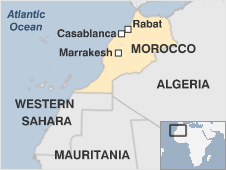 |
Strategically situated with both Atlantic and Mediterranean coastlines, but with a rugged mountainous interior, it stayed independent for centuries while developing a rich culture blended from Arab, Berber, European and African influences.
Morocco was a French protectorate from 1912 to 1956, when Sultan Mohammed became king. He was succeeded in 1961 by his son, Hassan II, who ruled for 38 years. He played a prominent role in the search for peace in the Middle East, given the large number of Israelis of Moroccan origin, but was criticised for suppressing domestic opposition.
|
A truth commission set up to investigate human rights violations during Hassan's reign has confirmed nearly 10,000 cases, ranging from death in detention to forced exile.
After his death in 1999 Hassan was succeeded by his son, who became King Mohammed VI and was seen as a moderniser. There has been some economic and social liberalisation, but the monarch has retained sweeping powers.
Morocco is bidding for membership of the European Union, its main trade partner, but there appears to be little enthusiasm for this within the bloc.
To the south, the status of Western Sahara remains unresolved. Morocco
annexed the territory in 1975 and a guerrilla war with Algerian-backed pro-independence forces ended in 1991. UN efforts have failed to break the political deadlock.
To the north, a dispute with Spain in 2002 over the tiny island of Perejil revived the issue of the sovereignty of Melilla and Ceuta. The small enclaves on the Mediterranean coast are surrounded by Morocco and have been administered by Madrid for centuries.
Morocco has been given the status of non-Nato ally by Washington, which has praised its support for the US-led war on terror. After deadly suicide bombings in Casablanca in 2003, Morocco launched a crackdown on suspected Islamic militants.
King: King Mohammed VI
Groomed for "kingship", as his late father King Hassan II referred to his upbringing, Mohammed VI became monarch in 1999.
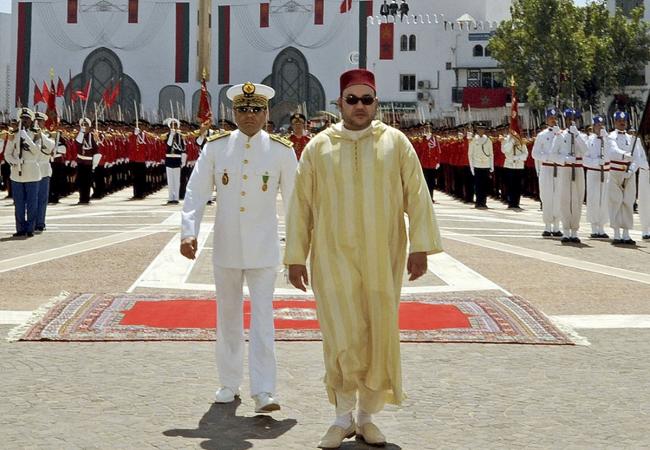

King Mohammed VI embarked on reforms
|
He initiated political and economic changes and an investigation into human rights abuses during his father's rule.
The king says the fight against poverty is a priority, earning him the name "guardian of the poor". Economic liberalisation has attracted foreign investment and officials point to better basic services in shanty towns and rural areas. But some non-government groups say little has changed, with poverty still widespread and unemployment remaining high.
A key reform has been the Mudawana, a law which grants more rights to women. The king has said it is in line with Koranic principles, but religious conservatives have opposed it.
Bomb attacks in Casablanca in 2003 prompted the enactment of new anti-terrorism laws and a reinvigorated campaign against extremists. But some rights groups say the measures have eroded human rights.
King Mohammed married computer engineer Salma Bennani in 2002. They have a son, Crown Prince Moulay Hassan, born in 2003, and a daughter, Princess Lalla Khadija, born in 2007.
Under the constitution, the king can dissolve parliament and dismiss or appoint the prime minister.
|
Prime minister: Abbas El Fassi
Mr El Fassi, leader of the conservative Istiqlal Party, took office in September 2007 after his party emerged as the largest in parliamentary elections.
Born in 1940, Mr El Fassi has served as a minister and diplomat since 1977, including a stint as ambassador to France in 1990-1994. He was minister of state in the coalition govermment of his predecessor, Driss Jettou, from 2002-2007.
His government also includes the Socialist Union of Popular Forces, the National Rally of Independents, and the Party of Progress and Socialism.
Morocco's private press is free to cover many previously-taboo issues, including social problems.

Satellite dishes are widely used in Morocco
|
But this freedom is not unbounded. Paris-based Reporters Without Borders, while noting "positive changes", has called for an overhaul of press laws. US-based Human Rights Watch says the press code "provides an arsenal of repressive tools". Western Sahara, the monarchy and corruption are all sensitive topics and self-censorship is commonplace.
Newspaper readership is limited by low literacy levels, and competition for advertising is intense.
The government owns, or has a stake in, RTM and 2M, Morocco's main TV networks. An expansion of private TV and radio services is under way. Broadcasters are tamer in their coverage of sensitive topics than the print media.
Satellite dishes are widely used, giving access to a range of foreign TV stations.
The press
Television
Radio
WESTERN SAHARA:
News agency
AFRICA | ASIA-PACIFIC | AMERICAS | EUROPE | MIDDLEEAST | SOUTHASIA
![]()
![]()
![]()
Mauritania Mauritius Morocco Mozambique Namibia Niger Nigeria Republic-of-congo Rwanda Sao-tome-and-principe Senegal Seychelles Sierra-leone Somalia South-africa Sudan Swaziland Tanzania The-gambia Togo Tunisia Uganda Australia Brunei Burma Cambodia China East-timor Fiji Indonesia Japan Kazakhstan Kiribati Kyrgyzstan Laos Malaysia Marshall-islands Micronesia Mongolia Nauru New-zealand North-korea Palau Papua-new-guinea Samoa Singapore Solomon-islands South-korea Taiwan Tajikistan Thailand The-philippines Tonga Turkmenistan Tuvalu Uzbekistan Vanuatu Vietnam Antigua-and-barbuda Belize Bolivia Brazil Canada Chile Colombia Costa-rica Cuba Dominica Dominican-republic Ecuador El-salvador Grenada Guatemala Guyana Haiti Honduras Jamaica Mexico Nicaragua St-kitts-and-nevis St-lucia Suriname Trinidad-and-tobago Uruguay Venezuela Albania Andorra Armenia Austria Azerbaijan Belarus Belgium Bosnia-hercegovina Bulgaria Croatia Cyprus Czech-republic Denmark Estonia Finland France Georgia Germany Greece Hungary Iceland Ireland Italy Latvia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Macedonia Malta Moldova Monaco Montenegro Norway Poland Portugal Russia San-marino Serbia Slovakia Slovenia Spain Sweden Algeria Egypt Iran Iraq Israel-and-palestinian-territories Jordan Kuwait Lebanon Libya Mauritania Oman Saudi-arabia Sudan Syria Tunisia United-arab-emirates Yemen Afghanistan Bangladesh Bhutan India Nepal Pakistan Sri-Lanka The-Maldive