Country profile: Uganda
Country profile: Uganda

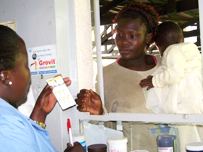
SECURING UGANDANS’ RIGHT TO ESSENTIAL MEDICINES
Working to ensure that Uganda’s population has access to quality essential medicines and health supplies by strengthening the national pharmaceutical supply system.
Health facilities and services in many developing countries usually suffer from insufficient basic infrastructure. Medicine supply stock-outs, accessibility, financial management, limited information management systems, quantification, procurement and storage are the leading drawbacks among others.
Since the late 1980s Uganda has rebounded from the abyss of civil war and economic catastrophe to become relatively peaceful stable and prosperous.
But the lives of hundreds of thousands of people in the north remain blighted by one of Africa's most brutal rebellions.
In the 1970s and 1980s Uganda was notorious for its human rights abuses first during the military dictatorship of Idi Amin
from 1971-79 and then after the return to power of Milton Obote who had been ousted by Amin.
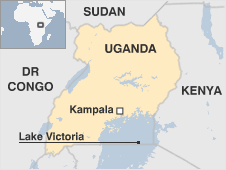
Overview
During this time up to half a million people were killed in state-sponsored violence.
 |
AT-A-GLANCE
Politics: Multi-party politics restored in 2005
Security: Government and Lord's Resistance Army (LRA) rebels have signed a truce aimed at ending a 19-year conflict
Economy: Uganda is vulnerable to changes in the world price of coffee its main export earner
International: Uganda has been actively involved in the DR Congo conflict. LRA leaders are wanted by the International Criminal Court for war crimes
|
Since becoming president in 1986 Yoweri Museveni has introduced democratic reforms and has been credited with substantially improving human rights notably by reducing abuses by the army and the police.
In addition Western-backed economic reforms produced solid growth and falls in inflation in the 1990s. However Mr Museveni has bemoaned his country's failure to industrialise.
The president came under fire for Uganda's military involvement along with five other countries in neighbouring DR Congo's 1998-2003 civil war. DR Congo accuses Uganda of maintaining its influence in the mineral-rich east of the country. Uganda says DR Congo has failed to disarm Ugandan rebels on its soil.
At home the cult-like Lord's Resistance Army (LRA) has perpetrated massacres and mutilations in the north for nearly two decades.
The group's leader has said he wants to run the country along the lines of the biblical ten commandments. The violence has displaced more than 1.6 million people and tens of thousands of civilians have been killed or kidnapped. The UN estimates that the group has abducted 20000 children.
The LRA and government signed a permanent cease-fire in February 2008 aimed at ending the long-running conflict.
However a final peace agreement remained elusive throughout 2008 with rebel leader Joseph Kony repeatedly failing to attend signing ceremonies.
The armies of Uganda Southern Sudan and DR Congo launched a coordinated offensive against LRA bases in December with the rebels requesting a ceasefire the following month.
Uganda has won praise for its vigorous campaign against HIV/Aids. This has helped to reduce the prevalence of the virus - which reached 30% in the 1990s - to single-digit figures.
Facts
- Full name: Republic of Uganda
- Population: 32.7 million (UN 2009)
- Capital: Kampala
- Area: 241038 sq km (93072 sq miles)
- Major languages: English (official) Swahili (official) Luganda various Bantu and Nilotic languages
- Major religions: Christianity Islam
- Life expectancy: 52 years (men) 53 years (women) (UN)
- Monetary unit: 1 Ugandan shilling = 100 cents
- Main exports: Coffee fish and fish products tea; tobacco cotton corn beans sesame
- GNI per capita: US $420 (World Bank 2008)
- Internet domain: .ug
- International dialling code: +256
Leaders
President: Yoweri Museveni
Yoweri Museveni Uganda's leader since 1986 was declared the winner of elections in February 2006 the first multi-party poll in 25 years.

Uganda's veteran leader Yoweri Museveni
|
Officials said he took 59% of the vote versus the 37% share of his main rival Kizza Besigye from the opposition Forum for Democratic Change.
Observers said the conduct of the poll was an improvement on the 2001 vote but critics accused the government of intimidating the opposition in the run-up. Dr Besigye has faced treason and rape charges - as well as terrorism charges in a military court - which his supporters say are politically motivated.
Parliament abolished a constitutional limit on presidential terms in 2005 paving the way for Mr Museveni to seek a third elected term and alarming some Western donors.
Severe restrictions on multi-party politics were imposed by Mr Museveni in 1986; only the president's "Movement" system was allowed to take part in elections.
Ugandans voted to lift the curbs in 2005 with the president maintaining that the country's factional rifts had been healed.
Born in western Uganda in 1944 Yoweri Museveni studied political science in Tanzania. There he became involved with the Front for the Liberation of Mozambique (Frelimo) and picked up the techniques of guerrilla warfare.
After a brief spell in the Ugandan government Mr Museveni fled to Tanzania in 1971 when Idi Amin toppled Milton Obote returning in 1980.
But when his party was defeated in elections which he said had been rigged he formed the National Resistance Army which brought him to power in 1986. Ten years later he won Uganda's first direct presidential election and was re-elected in 2001.
Media
Uganda is a pioneer in the liberalisation of the media in Africa. Private radio and TV have mushroomed since the government loosened controls in 1993.
By late 2006 the central region around Kampala was home to more than 40 FM radio stations and 10 TV stations. Rural radio stations serve various ethnic groups and there is a cluster of faith-based radios.
But the state sometimes criticises the conduct of private broadcasters. Some have been accused of raising ethnic tensions and of being negative in their reporting.
The authorities suspended broadcasts of a popular private station KFM for a time in August 2005 after it broadcast a debate about the death of a Sudanese former rebel leader.
Radio is the most popular medium. Public UBC Radio can be heard across the country in English and vernacular languages. BBC World Service is widely available on FM (101.3 in Kampala) and Radio France Internationale broadcasts on FM in the capital.
Although the print media are led by the state-owned New Vision newspaper it enjoys considerable independence and often publishes articles which criticise the government.
The press
Television
- UBC TV - public run by Uganda Broadcasting Corporation
- WBS - private operated by Wavah Broadcasting Service
- Pulse TV - private
- Nation TV (NTV) - private
- East Africa TV - private
Radio

AFRICA | ASIA-PACIFIC | AMERICAS | EUROPE | MIDDLEEAST | SOUTHASIA



Mauritania Mauritius Morocco Mozambique Namibia Niger Nigeria Republic-of-congo Rwanda Sao-tome-and-principe Senegal Seychelles Sierra-leone Somalia South-africa Sudan Swaziland Tanzania The-gambia Togo Tunisia Uganda Australia Brunei Burma Cambodia China East-timor Fiji Indonesia Japan Kazakhstan Kiribati Kyrgyzstan Laos Malaysia Marshall-islands Micronesia Mongolia Nauru New-zealand North-korea Palau Papua-new-guinea Samoa Singapore Solomon-islands South-korea Taiwan Tajikistan Thailand The-philippines Tonga Turkmenistan Tuvalu Uzbekistan Vanuatu Vietnam Antigua-and-barbuda Belize Bolivia Brazil Canada Chile Colombia Costa-rica Cuba Dominica Dominican-republic Ecuador El-salvador Grenada Guatemala Guyana Haiti Honduras Jamaica Mexico Nicaragua St-kitts-and-nevis St-lucia Suriname Trinidad-and-tobago Uruguay Venezuela Albania Andorra Armenia Austria Azerbaijan Belarus Belgium Bosnia-hercegovina Bulgaria Croatia Cyprus Czech-republic Denmark Estonia Finland France Georgia Germany Greece Hungary Iceland Ireland Italy Latvia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Macedonia Malta Moldova Monaco Montenegro Norway Poland Portugal Russia San-marino Serbia Slovakia Slovenia Spain Sweden Algeria Egypt Iran Iraq Israel-and-palestinian-territories Jordan Kuwait Lebanon Libya Mauritania Oman Saudi-arabia Sudan Syria Tunisia United-arab-emirates Yemen Afghanistan Bangladesh Bhutan India Nepal Pakistan Sri-Lanka The-Maldive