Generic Medicines
Taj Pharma is the largest generic pharmaceutical company in India. We hold top positions in different established markets worldwide generics markets..

 |
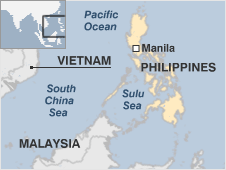 |
Much of the country is mountainous and prone to earthquakes and eruptions from around 20 active volcanoes. It is often buffeted by typhoons and other storms.
Two presidents of the Philippines were forced from office by "people power" in the space of 15 years.
The Philippines - a Spanish colony for more than three centuries and named after a 16th century Spanish king - was taken over by the US in the early 20th century after a protracted rebellion against rule from Madrid. Spanish and US influences remain strong especially in terms of language religion and government.
Self-rule in 1935 was followed by full independence in 1946 under a US-style constitution. President Ferdinand Marcos a close ally of the US imposed martial law in the early 1970s but was forced to step down in 1986 after mass demonstrations cost him the support of the armed forces.
Although the country has remained a democracy it has enjoyed little stability. President Joseph Estrada was forced out of office in 2001 after months of protests at his corrupt rule and there have been a number of coup attempts against his successor Gloria Arroyo.

Health Care products
|
On the southern island of Mindanao rebels have been fighting for a separate Islamic state within the mainly-Catholic country. The decades-long conflict has claimed more than 120 000 lives. Sporadic violence has continued despite a 2003 ceasefire and peace talks.
The Abu Sayyaf group on the island of Jolo has a history of violence towards hostages and the government has declared all-out war on it over its alliance with al-Qaeda.
Although it once boasted one of the region's best-performing economies the Philippines is saddled with a large national debt and tens of millions of people live in poverty. The economy is heavily dependent on the billions of dollars sent home each year by the huge Filipino overseas workforce.
The Philippines has the highest birth rate in Asia and forecasters say the population could double within three decades.
Governments generally avoid taking strong measures to curb the birth rate for fear of antagonising the Catholic Church which opposes artificial methods of contraception.
President: Gloria Macapagal Arroyo
Gloria Arroyo's efforts to tackle corruption and to focus on economic reform have been undermined by a string of scandals.
Philippines
Health
|
The president won a second six-year term in June 2004 defeating her main rival the film star Fernando Poe Junior.
But a year later her popularity rating had fallen to a record low amid opposition claims that she cheated in the 2004 elections. Opponents also levelled corruption allegations against her husband and other family members.
She apologised to the nation for talking to an election official about her hopes for victory in the run-up to the 2004 poll but denied any wrongdoing. Two subsequent attempts to impeach her have failed.
Mrs Arroyo faces the challenge of delivering on her promises to create jobs and to improve living standards. Social and economic reforms introduced during her first term did little to ease poverty and the country's debt burden.
She advocates constitutional reform proposing to swap the country's US-style presidential system for a parliamentary government.
She has taken a strong line on law and order and allied herself closely to US President George W Bush's "war on terror".
Gloria Arroyo comes from the political elite in the Philippines. She is an economist whose father was president in the early 1960s.
She was elevated from vice president to president in 2001 after protests led to the ousting of her predecessor Joseph Estrada. In 2003 she survived an attempt by military mutineers to unseat her.
She is keen to emphasise her Christian faith. Observers contrasted her approach with the hard-drinking lifestyle favoured by President Estrada.
The Philippines has a two-house legislature - the Congress - which comprises a House of Representatives with up to 250 members and a 24-member Senate.
Powerful commercial interests control or influence much of the media.
The lively TV scene is dominated by the free-to-air networks ABS-CBN and GMA which attract the lion's share of viewing. Some Manila-based networks broadcast in local languages. The country has a well-developed cable TV system.
Films comedies and entertainment programmes attract the largest audiences. Many TV broadcasters also operate radio networks. There are more than 700 FM and mediumwave (AM) radio stations most of them commercial.
Press freedom is guaranteed under the 1987 constitution. The private press is vigorous with tabloid newspapers being prone to sensationalism.
However violence against media workers is a problem. Reporters Without Borders noted in 2008 that "constant threats and physical attacks make some regions particularly Mindanao island dangerous areas".
By 2007 there were 14 million internet users (ITU).
The press
Television
Radio
News agency
Philippines News Agency - government-run
AFRICA | ASIA-PACIFIC | AMERICAS | EUROPE | MIDDLEEAST | SOUTHASIA
![]()
![]()
![]()
Mauritania Mauritius Morocco Mozambique Namibia Niger Nigeria Republic-of-congo Rwanda Sao-tome-and-principe Senegal Seychelles Sierra-leone Somalia South-africa Sudan Swaziland Tanzania The-gambia Togo Tunisia Uganda Australia Brunei Burma Cambodia China East-timor Fiji Indonesia Japan Kazakhstan Kiribati Kyrgyzstan Laos Malaysia Marshall-islands Micronesia Mongolia Nauru New-zealand North-korea Palau Papua-new-guinea Samoa Singapore Solomon-islands South-korea Taiwan Tajikistan Thailand The-philippines Tonga Turkmenistan Tuvalu Uzbekistan Vanuatu Vietnam Antigua-and-barbuda Belize Bolivia Brazil Canada Chile Colombia Costa-rica Cuba Dominica Dominican-republic Ecuador El-salvador Grenada Guatemala Guyana Haiti Honduras Jamaica Mexico Nicaragua St-kitts-and-nevis St-lucia Suriname Trinidad-and-tobago Uruguay Venezuela Albania Andorra Armenia Austria Azerbaijan Belarus Belgium Bosnia-hercegovina Bulgaria Croatia Cyprus Czech-republic Denmark Estonia Finland France Georgia Germany Greece Hungary Iceland Ireland Italy Latvia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Macedonia Malta Moldova Monaco Montenegro Norway Poland Portugal Russia San-marino Serbia Slovakia Slovenia Spain Sweden Algeria Egypt Iran Iraq Israel-and-palestinian-territories Jordan Kuwait Lebanon Libya Mauritania Oman Saudi-arabia Sudan Syria Tunisia United-arab-emirates Yemen Afghanistan Bangladesh Bhutan India Nepal Pakistan Sri-Lanka The-Maldive